MCP's Lifecycle Management Services Have Come A Long Way in Just Five Years
According to the old saying, time flies when one is having fun. The adage also applies when a new business unit is being built.
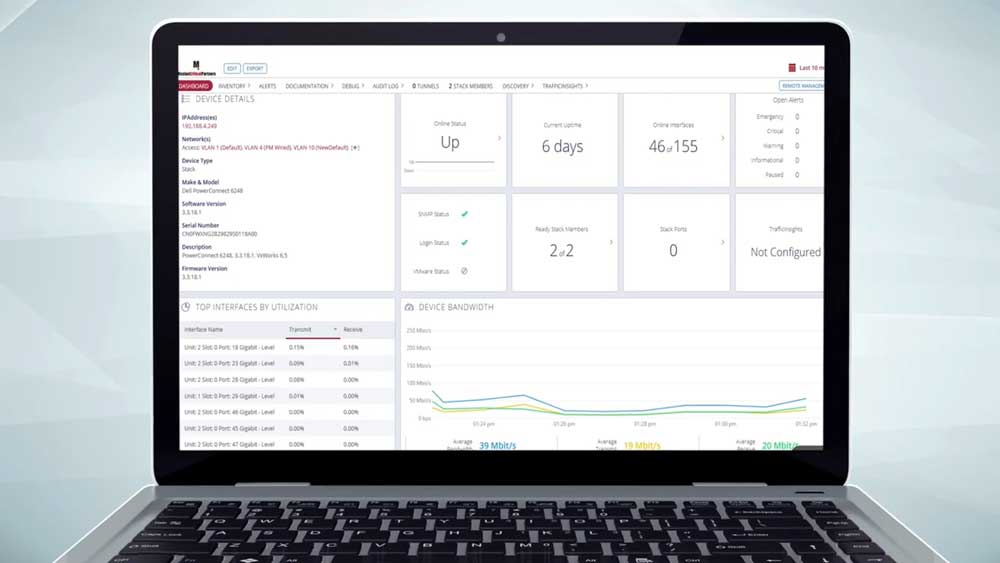
A little more than five years ago—has it really been that long?—MCP landed its first network monitoring contract, which marked the birth of our Lifecycle Management Services division. The initial concept for MCP to get involved in this business was the brainchild of Dave Boyce, with a helpful push from Brian Bark. It all started when the Pennsylvania Region 13 Task Force decided that once their Emergency Services Internet Protocol Network (ESInet) was complete, the region needed to monitor the ESInet. Because MCP subject matter experts had designed and deployed the network, Region 13 asked us for help in securing a monitoring service. The search didn’t go well. There weren’t many options, and those that were qualified to do the work were seeking fees that were markedly cost prohibitive, or they wanted to monitor only a specific network segment.
That’s when the proverbial lightbulb went on. “Maybe there’s a way that we can do this ourselves,” Dave said.