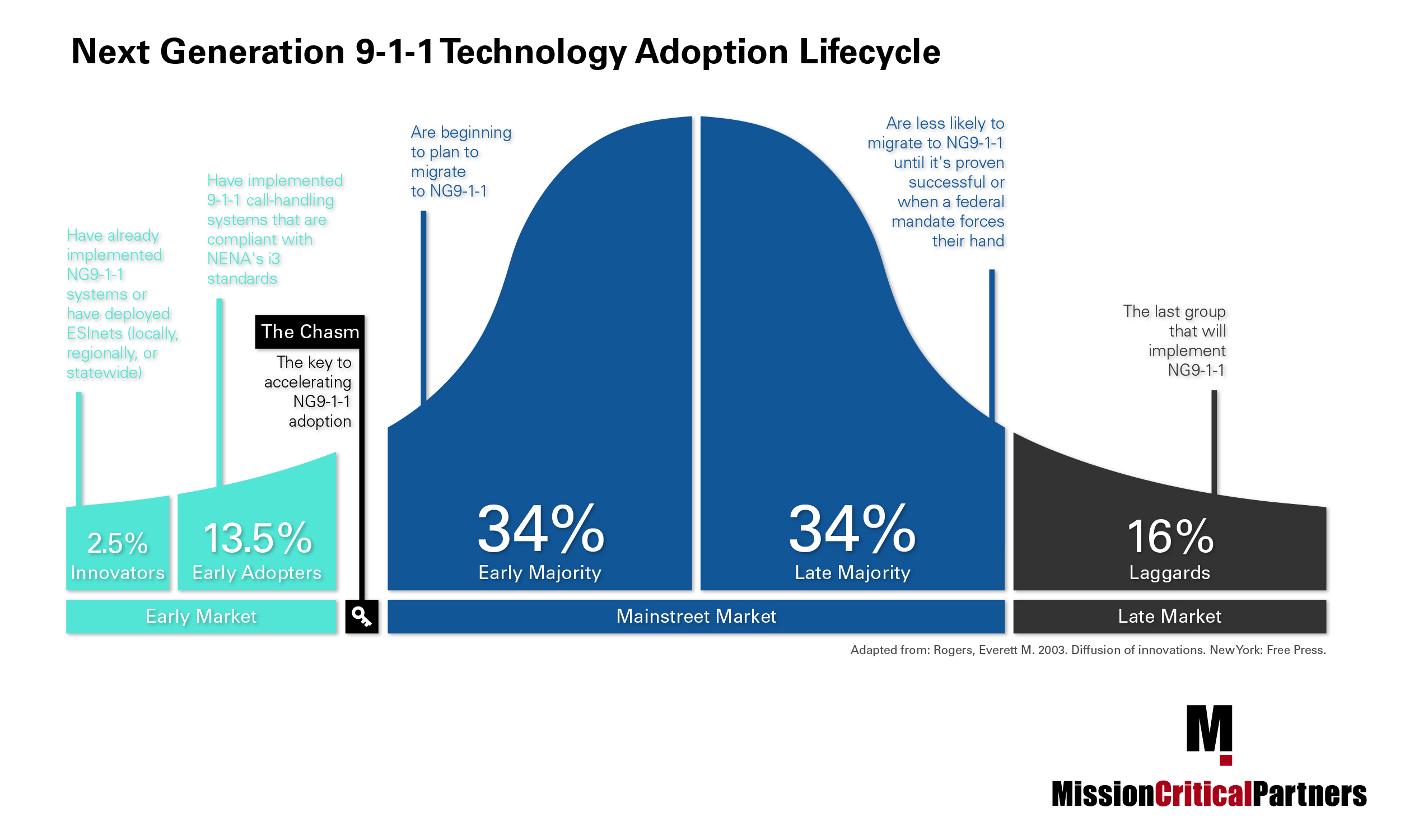
The Critical Role of Standards for NG911 Implementation
Throughout the design, development, and implementation of Next Generation 911 (NG911), one fundamental requirement has remained true: to achieve interoperability across the entire public safety communications ecosystem, NG911 implementations must adhere to a standard. For many years now, the 911 community has agreed that the NG911 standard is the National Emergency Number Association’s (NENA) Detailed Functional and Interface Standards for the NENA i3 Solution[1], commonly known as "NENA i3."
The first version of the standard, NENA 08-003, was ratified in June 2011. Since then, the standard was renumbered as NENA-STA-010.2-2016 when it was last updated in 2016. Later this year, NENA plans to revise the standard yet again expects American National Standards Institute (ANSI) ratification once again.