An Introduction to Data Lakes for Public Safety and Justice Organizations
Imagine that you're a fisherman, and you need to catch a large volume and wide variety of fish. Now imagine that the fish scatter amongst numerous rivers and streams, a situation that makes your task far more time-consuming and difficult. Moreover, you risk missing some types of fish you need to catch to fulfill your mission, either because you can't find them or you run out of time.
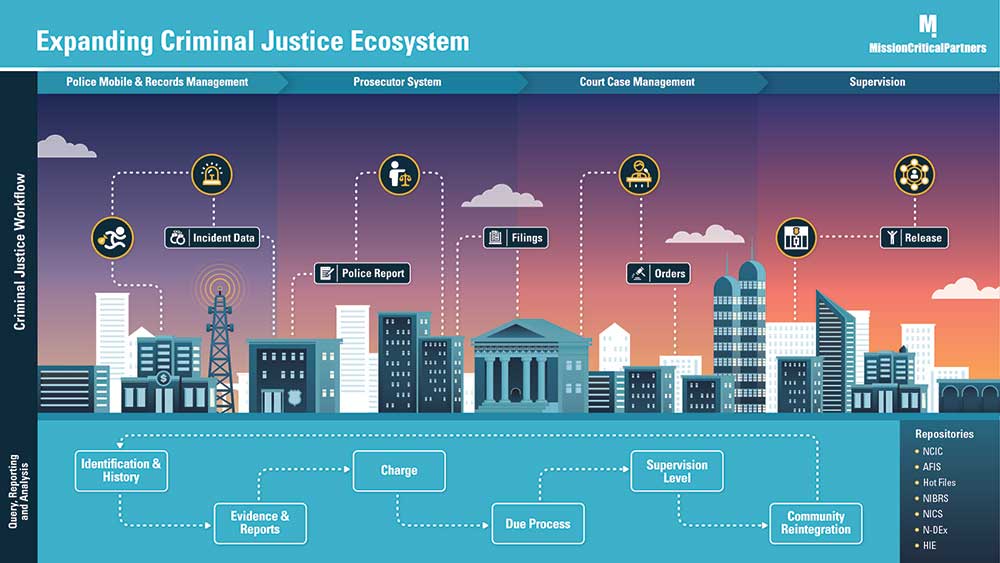
This metaphor describes the environment in which public safety and justice organizations are working today. Many systems exist that generate or store information vital to investigators, prosecutors, judges, and corrections officials. However, many are unable to access the information when they need to do so. That's because siloes exist in these systems, making it incredibly challenging for the individual entities that comprise the public safety and justice ecosystem — the 911 community, law enforcement, prosecutors, the courts, and jails/prisons — to exchange data. Siloed systems are analogous to the rivers and streams in our metaphor.